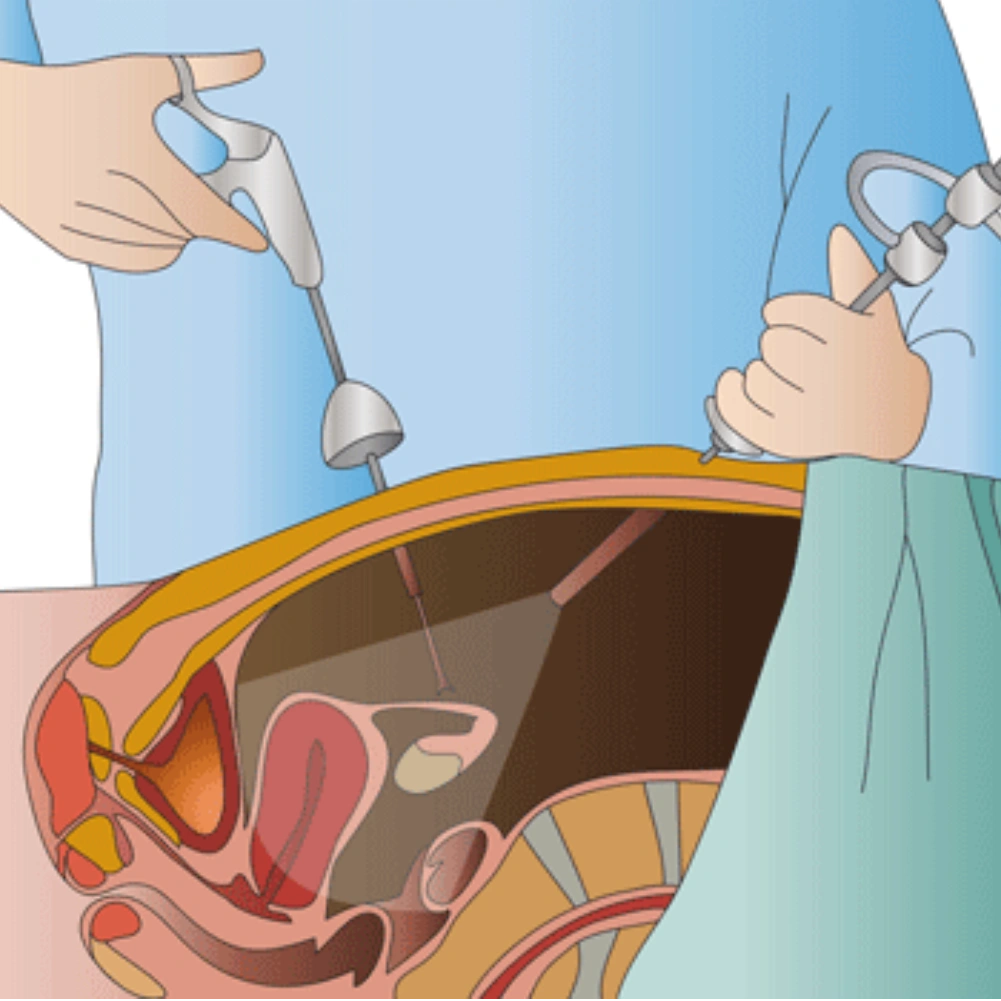
LAPROSCOPY:
WHAT IT IS AND HOW IT WORKS
This involves making small incisions in the abdomen to insert a laparoscope. Used for complex urological procedures such as kidney removal, removal of renal cysts and prostate surgery.
Laparoscopy results in less scarring, less pain and faster recovery than traditional open surgery.
Minimally invasive
Cicatrización reducida
Faster recovery
Improved visualization
Reduced bleeding
Regreso a las actividades cotidianas más rápido
LAPROSCOPIA
Types of laparoscopic procedures in urology: Laparoscopy is used for a wide range of urological procedures, including:
Laparoscopic Nephrectomy: This procedure consists of the removal of a kidney, either for kidney donation or to treat renal conditions such as tumors or non-functioning kidneys.
Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy: In this procedure, only the affected part of the kidney is removed, preserving healthy kidney tissue.
Laparoscopic prostatectomy: This is a minimally invasive approach to remove the prostate gland for the treatment of prostate cancer.
Laparoscopic adrenalectomy: This surgery is performed to remove the adrenal gland for conditions such as tumors or hyperfunctioning glands.
Laparoscopic Pyeloplasty: It is a procedure to correct an obstruction in the ureteropelvic junction (UPJ) that causes the obstruction of urine flow from the kidney to the ureter.
Laparoscopic cystectomy: This procedure consists of the removal of the bladder for conditions such as bladder cancer.
Laparoendoscopic in situ surgery (LESS): LESS is a specialized form of laparoscopy in which all instruments and the laparoscope are inserted through a single small incision, usually located in the umbilicus (belly button). This method leaves less visible scarring and further enhances the cosmetic result.
Robotic-assisted laparoscopy: In some cases, laparoscopic procedures can be performed with the assistance of robotic systems. The surgeon controls robotic arms equipped with surgical instruments, providing greater dexterity and precision during the procedure.
Advantages of robotic-assisted laparoscopy: Robotic technology allows for more intricate movements and better ergonomics for the surgeon, which translates into better results, less surgeon fatigue and greater patient safety.
Training and experience: Performing laparoscopic procedures requires specialized training and experience for urologists to ensure safe and satisfactory results. Laparoscopic urologists receive extensive training and gain experience through supervised practice.
Patient selection: Not all patients are candidates for laparoscopic procedures, as individual medical conditions and patient characteristics may influence the choice of surgical approach. A thorough evaluation and discussion with the urologist will determine the most appropriate treatment plan for each patient.
Technological advances: Laparoscopic instruments and imaging technology continue to evolve, leading to further improvements in the accuracy and capabilities of laparoscopic procedures.
Research and evidence: Laparoscopy in urology has been extensively studied, and a considerable body of evidence supports its efficacy and safety for a variety of urologic conditions.
Laparoscopy has transformed urological surgery by offering patients less invasive and highly effective treatment options. The continued advancement of laparoscopic techniques, including robotic-assisted approaches, ensures that patients receive state-of-the-art care with better outcomes and faster recovery times. As with any medical procedure, patients should consult a qualified urologist to determine the most appropriate surgical approach for their specific condition.