PERCUTANEOUS:
WHAT IT IS AND HOW IT WORKS
Procedures involve accessing organs through the skin using a needle or catheter. Used to treat conditions such as large kidney stones or certain kidney tumours.
These procedures are less invasive, resulting in shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times.
Minimally invasive
Faster recovery
Reduced risk of infection
Less blood loss
Improved quality of life
Effective stone removal
PERCUTANEOUS:
Percutaneous procedures consist of accessing organs or internal structures through the skin by means of a needle or catheter, without the need for large incisions. The term "percutaneous" comes from Latin, where "per" means through and "cutaneous" refers to the skin. These minimally invasive techniques have revolutionized urological care, providing safer and more effective treatment options for a variety of conditions.
Common percutaneous procedures in urology include:
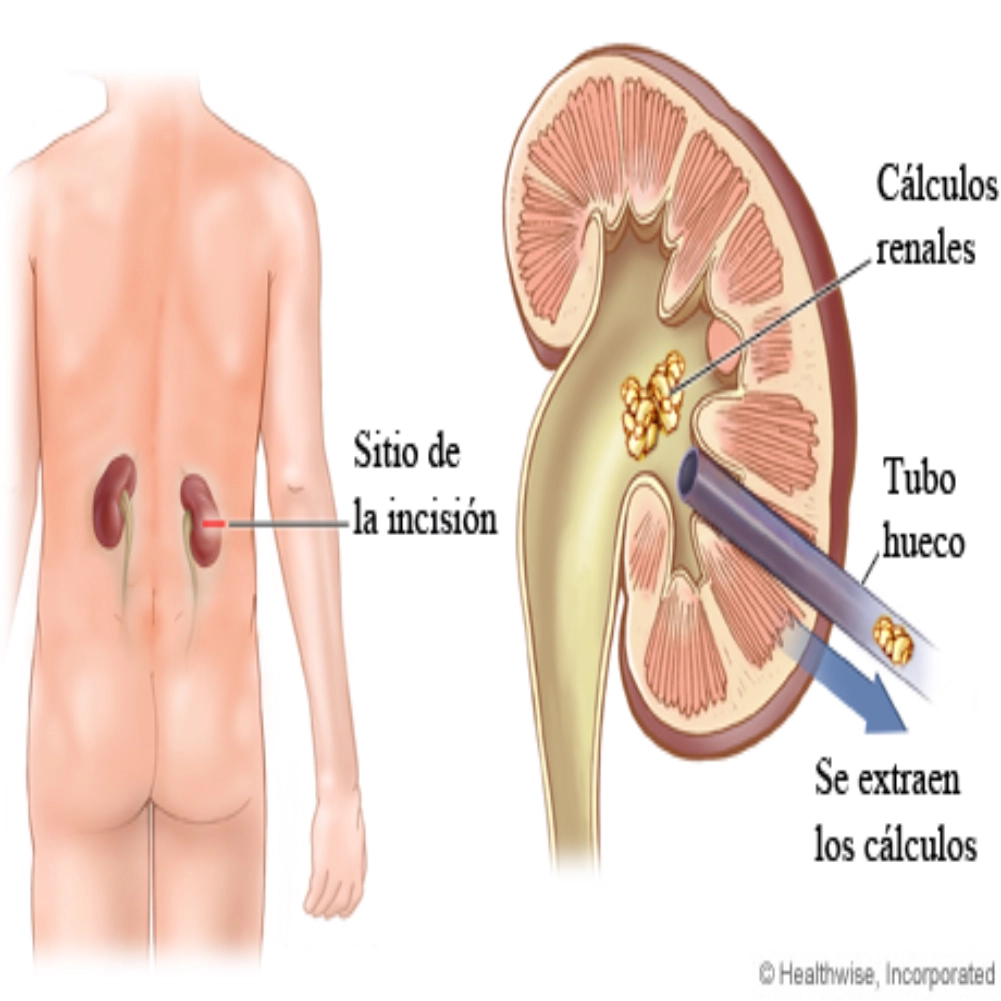
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL): PCNL is a procedure used to remove large kidney stones that are difficult to treat with other methods, such as shock wave lithotripsy or ureteroscopy. A small incision is made in the patient's back and a hollow needle is inserted directly into the kidney to access the stone. Through this access, specialized instruments such as lasers, forceps or ultrasound probes are used to fragment and remove the kidney stone.
Percutaneous nephrostomy: This procedure involves placing a catheter directly into the kidney through the skin to drain urine when the normal drainage pathway is blocked. It is usually used in cases of severe kidney obstruction, such as that caused by kidney stones or tumors.
Percutaneous kidney biopsy: Percutaneous kidney biopsy is performed to obtain a small sample of kidney tissue for diagnostic purposes. A needle is inserted into the kidney through the skin to collect tissue samples, which helps diagnose kidney disease and determine appropriate treatment plans.
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA): In urology, PTA is used to treat narrowing or blockages in the blood vessels that supply the kidneys (renal arteries). A catheter with a deflated balloon at the tip is threaded through the blood vessels to the site of the blockage. Once in position, the balloon is inflated, opening the narrowed area and restoring blood flow.
Percutaneous drainage: This procedure consists of placing a catheter through the skin to drain fluid accumulations or abscesses in or around the urinary system, such as perirenal or perinephric abscesses.